- Is a commission rebate legal in Ontario? →
- How much will I actually save? →
- When do I receive my rebate? →
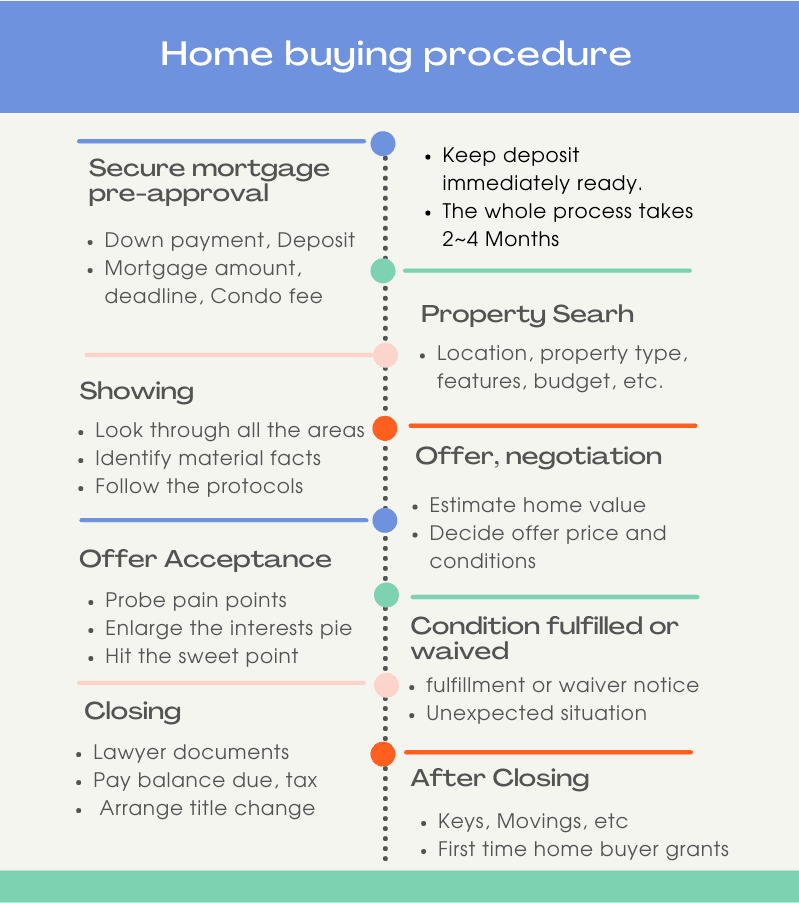
The first step of buying a house in Toronto is to secure your mortgage pre-approval
Locate the property meeting your demand (property type, location, features, budget, etc.)
Place an offer (normally with conditions)
The seller accepts the offer (normally after negotiation)
Fulfill or waive the conditions (arrange the financial funds, home inspections, etc) and hire a lawyer for the title and non title search to ensure the property is good in the title and with no working orders
On the completion date, pay the balance due, tax, and arrange the title change
The whole process for residential properties is normally ranging from 2-4 months. Tax for resales home involves land transfer tax (additional equivalent amount of land transfer tax for Toronto City) without HST. Tax for new home purchases involves HST without land transfer tax
The average house cost in GTA is $1M in early 2021. Before you decide to buy a house, you may need to know how much downpayment you prepare and how much you could afford to pay for a mortgage.
Generally, the down payment starts from 20% of the total amount from the main lenders which require more strict qualifications.
You also need to consider the other costs associated with the house purchase, such as land transfer tax, closing adjustment, lawyer fees, and others like legal fees, home inspector, insurance, home appraisal fee, etc. Those extra costs stand roughly around 3% of the home purchase price.
After a house purchase, you would budget the housing cost since owning a home in Canada is not cheap either.
Definition: A legal agreement by which a bank or other creditor lends money at interest in exchange for taking the title of the debtor's property, with the condition that the conveyance of title becomes void upon the payment of the debt.
Fixed-rate mortgage: the rate of interest is fixed throughout the term of the loan
Variable-rate mortgage: the interest rate is adjusted periodically, based on the prime rate, to reflect market conditions.
Interest rates: largely determined by market i.e.supply and demand, some other factors have impacts as well
Canada Prime Rate: The prime rate, also known as the prime lending rate, is the annual interest rate that Canada's major banks and financial institutions use to set interest rates for variable loans and lines of credit, including variable-rate mortgages.
Gross Debt Service (GDS) ratio: GDS ratio is the percentage of your monthly household income that covers your housing costs. It normally ranges from 27% to 32%
Total Debt Service (TDS) ratio: TDS ratio covers your other debt as well, normally range from 37% to 40%
In addition, for condominium purchases, the lender adds an additional 50% of the monthly maintenance fee to calculate the GDS ratio.
Mortgage broker fees: Normally paid by the lender in residential mortgages from major lenders. You still need to confirm with your mortgage broker first.
Legal fees: Paid by the buyer, normally combined with the fee for the transfer of title.
Appraisal fees: Requested by the lender, but in many cases, paid by borrowers. You should confirm this as well.
Pre-approval means that a lender has stated that you qualify for a mortgage loan based on the information you have provided, and it is subject to certain conditions. A mortgage pre-approval often specifies a term, interest rate, and principal amount.
Pre-qualifying is only the first step in the process before pre-approval mortgage.
Before you start hunting for a home, please take a quick check on the following questions. It would help you streamline your thoughts:
Is your budget fixed or have more room to move up?
Are you aware of the costs that come along with purchasing a home?
When do you need the home? The desired closing date?
Is there a definite time the transaction must be done?
Have you already sold your property, if you have one?
Do you plan to make improvements or renovations after buying?
Do you consider any other neighborhoods if the desired one is not met?
What kind of property requirements you must have, and what are negotiable? Those requirements include location, type of property square foot, number of bedrooms and bathrooms, lot size, yard size and view, kitchen and bathroom features, garage size, school, public transportation, highway access, main floor height, t-junction, age of home, home-style, stories, basement finished or not and with walkout or not, decorations, floor type, etc.
With the technology advancement, searching for a property online becomes much easier and free. More and more buyers are less relying on the agents to find the matching properties in a traditional way.
There are many websites offering the home search function, Realsav.com is one of them. All those websites are using the same data resources, i.e. MLS, where most sellers are listing their home.
MLS Stands for Multiple Listing Services. MLS Toronto covers the listings in GTA. Its listings sound like the entire original book, while Realtor.com and other websites are nationwide listings and their listings are more like a shorter version.
MLS listings may contain exclusive information such as listing agent remarks and notes, the commission to the cooperating brokerage, relevant documents, and sensitive information.
Structure style, Interior property conditions, exterior property conditions, front yard, and backyard, basement, garage, deck, etc, location in the neighborhood, neighborhood-style and amenities, closeness to school, and school ranking if you have kids
Material facts are the factors that may influence the home buyers' decision on the house purchase. Material facts can be latent or patent.
Patent material facts are visible and easy to be identified with observation. Latent material facts are either hidden or unobvious to the eyes who are not trained and who have not gained enough knowledge to identify.
There are a lot of areas you need to pay attention to. It commonly includes Knob-and-tube, roof leaks, foundation, grow-up, etc. Heritage property
The agreement that homebuyer prepared is called an offer before the acceptance from the seller, after that, it is a binding agreement.
A conditional offer is a buyer includes some conditions like financing, home inspection, which protects the buyer’s interest. If conditions are met, the deal moves forward, if not, the deal falls through. The buyer can walk away with no penalties.
A firm offer means no condition included in the offer, it happens often in the bidding war when a buyer wants to win a house.
A number of forms are used to document the contracts. OREA forms are commonly used in Canada. We’ve listed all the commonly used forms with explanations and samples. It is important for you to understand well before signing.
There are a number of factors to consider before you offer on a property. Those factors include the house itself, the economic condition, the anticipation of market trend, your’s and the seller’s situation, etc. How to estimate a home value needs knowledge and experience. Realtors mainly refer to CMA Comparative Market Analysis, of which the comparable property is the key.
You identify a house you like and want to make an offer
The real estate agent assists you on the offer details including the offer price, deposit, irrevocable date, completion date, chattels, fixtures, conditions, etc. You decide what your offer will be.
You sign off the offer after review, and the offer is registered with the seller’s brokerage.
Accepts the offer. The offer is signed back, the agreement becomes binding to both parties. You are ready to move on to the next step according to the contract.
The seller makes a counteroffer. You can either accept, make a counteroffer, or walk away.
The seller rejects the offer. You could then try to make a more appealing offer (if your budget allows) or move on to find another house
Special Consideration on bully offer and bidding war
Sometimes, you would like to consider a bully offer to circumvent the competition and win a house, especially when you are in the bidding war in the hot market. You would probably think through all the pros and cons before making such a decision.
After due diligence, if you are satisfied, the salesperson provides notice of fulfillment to the seller’s agent, and the deal proceeds.
If you are not satisfied, you could either walk away from the deal and get your deposit back by the mutual release signed with both parties; Or you may waive the offer and proceed with the deal if such a clause is included in the agreement.
Yes, but you need the change accepted and signed by the seller to be binding. Any change to the terms agreed upon should be written in a new document. All other terms of the accepted offer remain the same.
If the seller doesn’t agree to the amendment, the original terms remain in effect.
An amendment to the agreement of purchase and sale is used for this purpose. An amendment may be requested by either a seller or a buyer.
A final walk through the house
Arranging for delivery of closing funds to the seller's lawyer.
Registering the transfer and mortgage.
Getting the keys for your new home.
Please refer to the House closing checklist in Ontario for details
Land transfer tax, legal fees, disbursements, property tax adjustments, unmetered utilities, and fuel if any, are apportioned by the buyer. For condo buyers, maintenance fees may be involved.
Closing costs of buying a home has a comprehensive description on it
Takeaways
Avoid an end-of-month or end-of-week closing.
The Canadian government provides Incentive for the First-Time Home Buyer
5% for buying a resale home.
5% for buying new or resale mobile/manufactured homes.
However, if you decide to sell the home in the future, you need to pay back the same percentage of the value of the home.
There are a number of rules and qualifications applied. Please check your mortgage specialist on your eligibility. You could also refer to First-Time Home Buyer Incentive for more info.
As a first-time home buyer, you may also be qualified for the tax credit for purchasing a home. There is also a list of criteria that need to be fulfilled, and please check with your accountant before your next tax filing. Here is a quick reference to CRA Home Buyers Tax Rebate
First-time home buyers may qualify for a rebate with a maximum of $4000, but they have to meet the following requirements
The buyer must be a Canadian citizen or a permanent resident of Canada.
The buyer must be 18 years of age or older.
The buyer must occupy the home as a principal residence within nine months of registration.
The buyer cannot have owned a home anywhere in the world.
If the purchaser has a spouse, the spouse cannot have owned an eligible home or had any ownership interest in an eligible home anywhere in the world while he or she was the purchaser's spouse.
In addition, please check out the Home Buyers' Plan (HBP), GST/HST New Housing Rebate to see if you could get additional benefits.